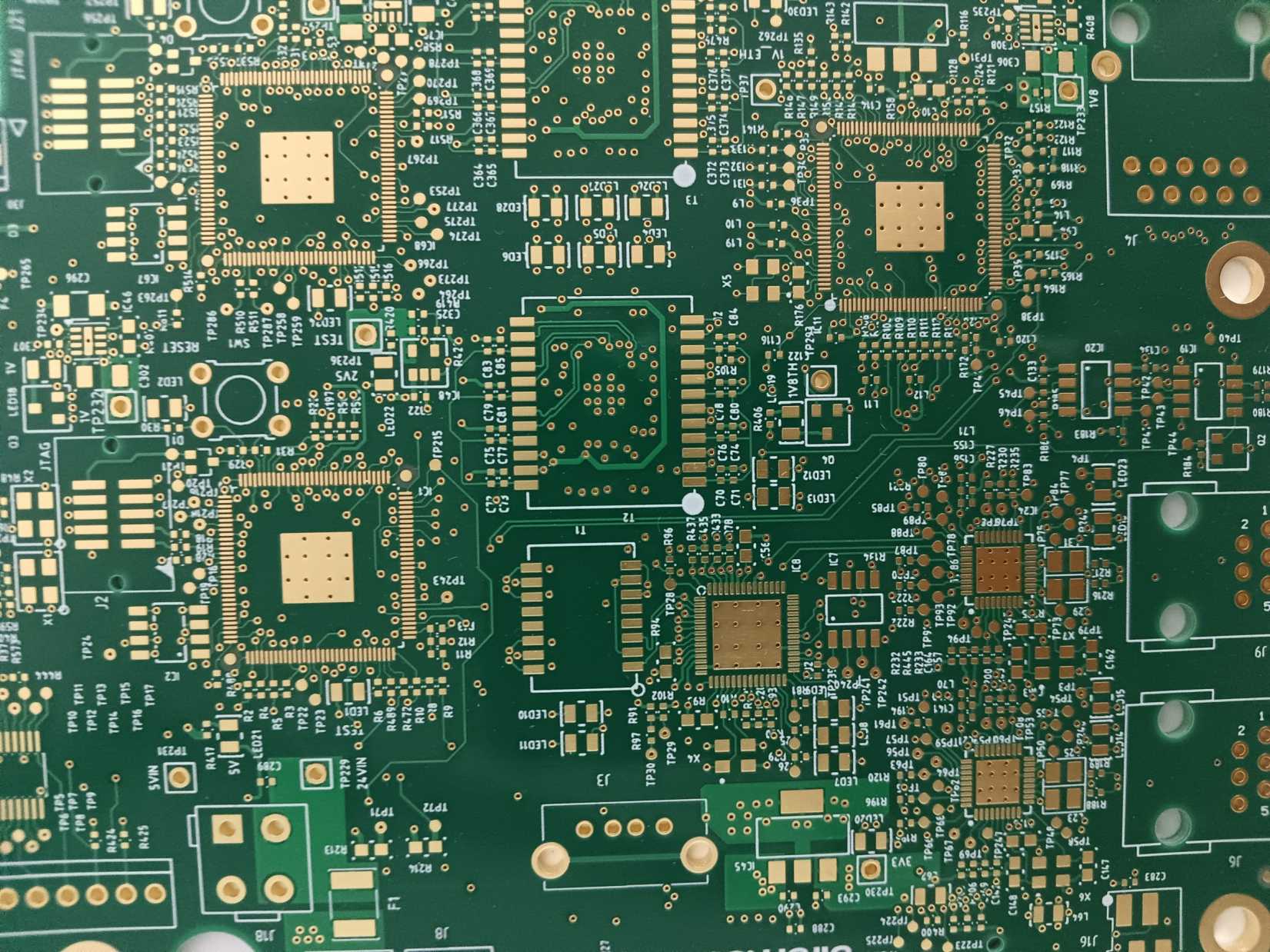
The application of high-frequency printed circuit boards is becoming more and more extensive, and in the design and manufacture of high-frequency printed circuit boards, signal interference is a key problem, if the design is not reasonable, it will seriously reduce the performance of electronic equipment.
There are several effective ways to prevent such interference:
1. Correct component layout when designing circuit boards
The component layout is one of the foundations. The design of high-frequency components is placed close to each other, and it is recommended to minimize the length of the signal traces. For example, in a communication module board assembly, the oscillator and the RF transceiver are adjacent. Separating analog and digital components is also crucial. This separation minimizes the risk of digital noise coupling into more sensitive analog signals.
2. The best traceroute
When it comes to circuit board routing, brevity and straightness are paramount. Antennas can be designed to grow and mean, reducing radiated and received interference. In addition, differential signals are used for high-speed signals. Differentials are generally less susceptible to external interference because the noise has the same effect on both signals and can be canceled out by the receiver.


3. The importance of signal isolation
By implementing effective physical barriers, such as copper pours and through-hole fences, sensitive signals can be isolated from noisy signals. For example, when laying out, if there is a high-power clock signal on the PCB, surround it with a ground plane or a row of vias to prevent it from interfering with other signals.
4. Effective power management
A stable and high-quality power supply is essential. Whereas, multiple power planes and decoupling capacitors are used in the layout. Decoupling capacitors are placed near the power pins of the component to effectively filter out high-frequency noise from the power supply. They act as a local energy reservoir and provide a clean-sided, high-quality power supply to the PCB components.
5. The grounding design of the circuit board
Rugged design of the grounding system. Low-frequency circuits should be grounded at a single point, but multi-point grounding for high-frequency circuits is more effective. The aim is to ensure that the ground plane is continuous and has low resistance, which minimizes the loop of the ground, which can lead to electromagnetic interference.
In summary: By following these techniques in the design, designers can significantly reduce signal interference in high-frequency PCBs, resulting in more reliable and high-performance electronic product quality.